Before we begin...there is no quantum supremacy (Oct 1, 2019)
Daniel Lidar, professor of electrical engineering, chemistry, physics and astronomy at the University of Southern California, says none of the currently available quantum computers can do something that a classical computer cannot. “I think what’s confusing here is the disconnect between the hype in the media and the reality of experimental quantum computing,” he says. “With D-wave computers, you can solve non-trivial problems, but you can’t yet do it with the quantum speed-up relative to every conceivable classical algorithm, and they can only solve certain problems faster than some state-of-the-art methods,” he elaborates. However, Lidar adds, this in itself is interesting, as it “tells us we’re probably on the right track, but not there yet”.
Our point of view is that quantum computers are good enough to learn from, and to see problem spaces differently. To inspire innovation, creativity, and fresh approaches to unlocking greater productivity, creating new products, and optimizing outcomes.
We do agree that there are at least a dozen issues preventing today's quantum computers from being scaled into a monolithic, distributed, fault tolerant, error correcting quantum computing system.
We do agree that there are at least a dozen issues preventing today's quantum computers from being scaled into a monolithic, distributed, fault tolerant, error correcting quantum computing system.
D-Wave Systems - Quantum Annealer
D-Wave Systems designs, builds, sells, and provides shared access to commercial superconducting qubit quantum computers and an operating environment called Leap & Ocean
October 7, 2019, D-Wave Systems delivers a less noisy version of the 2000Q via its cloud service, Leap. Based on this article, and discussions at the D-Wave User Group conference in Newport, RI in September 2019, a less noisy solution allows for better and faster solutions. The annealing process is an analog one (forward and reverse, with multiple settings and parameters) which provides a complex, somewhat mechanical and 'trial and error' way to solve unconstrained quadratic optimization problems with binary variables, or QUBO problems.
D-Wave sold its 5,000 qubit Advantage system to LLNL as announced on September 24, 2019.
https://www.cnet.com/news/nuclear-weapons-lab-buys-d-wave-next-gen-quantum-computer/
I wonder what we will be able to accomplish with this new, significantly more powerful technology platform.
tay tuned for the next iteration of the D-Wave quantum annealing technology. Codenamed Pegasus, and with a brand name of D-Wave Advantage, it contains over 5,000 qubits, more connectivity between qubits, and less noise. This should deliver another significant speed-up over the upgraded 2000Q.
D-Wave sold its 5,000 qubit Advantage system to LLNL as announced on September 24, 2019.
https://www.cnet.com/news/nuclear-weapons-lab-buys-d-wave-next-gen-quantum-computer/
I wonder what we will be able to accomplish with this new, significantly more powerful technology platform.
tay tuned for the next iteration of the D-Wave quantum annealing technology. Codenamed Pegasus, and with a brand name of D-Wave Advantage, it contains over 5,000 qubits, more connectivity between qubits, and less noise. This should deliver another significant speed-up over the upgraded 2000Q.
On May 15, 2019, D-Wave announced cloud access (via Leap) to its lower-noise D-Wave 2000Q processor. Although I have not read the research article yet, it states a 25x speed-up on spin glass applications. As stated, "the lower-noise processor demonstrates improved performance, precision, and impact on quantum effects by reducing environmental noise in quantum annealing systems."
D-Wave Systems provides hardware, software, services and a shared operating environment for clients.
They publish and train on interesting use cases across multiple domains.
D-Wave Systems provides hardware, software, services and a shared operating environment for clients.
They publish and train on interesting use cases across multiple domains.
D-Wave LEAP (TM) quantum cloud service is now available in 33 new countries, including all 28 member states of the European Union, Japan, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland, which includes access to the D-Wave 2000Q (TM) system and its Quantum Application Environment (QAE). Just read the latest addition to LEAP (TM) is a processor with lower noise ratios, that speeds up at least one algorithm 25 times (citation needed).
IBM Corp. - Superconducting Qubits
IBM Corporation makes available quantum computers through the IBM Q Experience (available via IBM Cloud).
IBM has ~100 partners in the IBM Q Network, and has 10 quantum computers available via IBM Cloud, and 2 more advanced systems (largest with 53 qubits). Source: Arvind Krishna, January 2020
IBM's 14th quantum computer: 53 qubits; while IBM's 9 - 13th systems: 20 qubits.
ARMONK, N.Y., Sept. 18, 2019 /PRNewswire/ "Within one month, IBM's commercially available quantum fleet will grow to 14 systems, including a new 53-qubit quantum computer, the single largest universal quantum system made available for external access in the industry, to date."
How powerful is the IBM Q System One, with their latest, 4th generation 20 Qubit processor? One way to tell is the Quantum Volume (an IBM measurement procedure to determine system power in solving problems).
IBM Q System One (with 20 Qubits, 4th generation) = 16
Current IBM Q Experience System (with 20 Qubits, 3rd generation) = 8
Source: https://www.rdmag.com/news/2019/03/ibm-achieves-highest-quantum-volume-date-establishes-roadmap-reaching-quantum-advantage
IBM has ~100 partners in the IBM Q Network, and has 10 quantum computers available via IBM Cloud, and 2 more advanced systems (largest with 53 qubits). Source: Arvind Krishna, January 2020
IBM's 14th quantum computer: 53 qubits; while IBM's 9 - 13th systems: 20 qubits.
ARMONK, N.Y., Sept. 18, 2019 /PRNewswire/ "Within one month, IBM's commercially available quantum fleet will grow to 14 systems, including a new 53-qubit quantum computer, the single largest universal quantum system made available for external access in the industry, to date."
How powerful is the IBM Q System One, with their latest, 4th generation 20 Qubit processor? One way to tell is the Quantum Volume (an IBM measurement procedure to determine system power in solving problems).
IBM Q System One (with 20 Qubits, 4th generation) = 16
Current IBM Q Experience System (with 20 Qubits, 3rd generation) = 8
Source: https://www.rdmag.com/news/2019/03/ibm-achieves-highest-quantum-volume-date-establishes-roadmap-reaching-quantum-advantage
Our team signed up and just ran our first experiment.
Signup and execution took about 15 minutes (execution 1,024 times took just under 4 minutes)
The QASM editor requires programming (Python?), and the composer editor uses gates, barriers and operations (e.g., measurement). Our experiment is the equivalent of flipping three coins multiple times, then measuring. Not sure we learned much about coins, but I do see quantum noise and better understand the composer interface (similar to Alibaba / CAS).
We also joined the IBM Qiskit Slack channel and see activity.
Please check back for more information...as we learn more
Signup and execution took about 15 minutes (execution 1,024 times took just under 4 minutes)
The QASM editor requires programming (Python?), and the composer editor uses gates, barriers and operations (e.g., measurement). Our experiment is the equivalent of flipping three coins multiple times, then measuring. Not sure we learned much about coins, but I do see quantum noise and better understand the composer interface (similar to Alibaba / CAS).
We also joined the IBM Qiskit Slack channel and see activity.
Please check back for more information...as we learn more
Alibaba - Superconducting Qubits
Alibaba Cloud & Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS)
Alibaba, via Aliyun ("Alibaba Cloud") subsidiary, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai) has launched an 11 Qubit quantum computing cloud service to enhance experimental research capabilities.
We have access to this computer service and have run our first experiment. Worked very fast.
In a Sept 25, 2018 interview with Jeff Zhang, Alibaba's chief technology officer and head of DAMO Academy research lab (with Yiting Sun of the MIT Technology Review), Zhang shared two key points: Alibaba wants to solve the engineering problems of quantum computing and develop a processor, and Alibaba is building a superconducting quantum computer in their Hangzhou headquarters (and wants to scale quantum computing).
Source:: https://www.technologyreview.com/s/612190/why-alibaba-is-investing-in-ai-chips-and-quantum-computing/
In a Sept 25, 2018 interview with Jeff Zhang, Alibaba's chief technology officer and head of DAMO Academy research lab (with Yiting Sun of the MIT Technology Review), Zhang shared two key points: Alibaba wants to solve the engineering problems of quantum computing and develop a processor, and Alibaba is building a superconducting quantum computer in their Hangzhou headquarters (and wants to scale quantum computing).
Source:: https://www.technologyreview.com/s/612190/why-alibaba-is-investing-in-ai-chips-and-quantum-computing/
In July 2019, we learn more from an Alibaba Quantum Lab Job Posting, found here:
"We are a full stack R&D program with an emphasis on building hardware and systems of superconducting quantum computers. For the 2019 hiring, priorities will be given to device-level theory and simulation, error-correction, quantum computer architecture, and experimental solid-state physics. Our measurement lab will be completed in early 2019. While we currently use our partners' facilities for fabrication, we will enjoy our own dedicated, well-equipped clean room, which is already under construction."
"The goal of Alibaba Quantum Laboratory (AQL) is to realize the revolutionary potentials of quantum computing. We are committed to this long-term mission and aspire to build a world-leading program in the next few years."
"We are a full stack R&D program with an emphasis on building hardware and systems of superconducting quantum computers. For the 2019 hiring, priorities will be given to device-level theory and simulation, error-correction, quantum computer architecture, and experimental solid-state physics. Our measurement lab will be completed in early 2019. While we currently use our partners' facilities for fabrication, we will enjoy our own dedicated, well-equipped clean room, which is already under construction."
"The goal of Alibaba Quantum Laboratory (AQL) is to realize the revolutionary potentials of quantum computing. We are committed to this long-term mission and aspire to build a world-leading program in the next few years."
Google - Superconducting Qubits
Google AI & CIRQ
Google is innovating both QC hardware and its usage to gain more effective capability.
- For example, allowing control circuits to operate ~2milliwatts, at 4 kelvins, enables scaling. Using less qubits with better connectivity provides more processing power. Not sure about error rates, but likely they are reducing them as well.
- October 2019: we read a 'bootleg' research paper that suggests Google used a new quantum processor named "Sycamore" which consists of a two-dimensional array of 54 transmon qubits, each connected to their 4 closest neighbors (in a rectangle), and cooled to 20 mK.
- Neven's law suggests that Google is achieving speed-up from both the processor, and learning how to use it.
According to an Independent article, "If Google’s leaked paper is to be believed...A calculation that would take a traditional supercomputer approximately 10,000 years to perform, took Google’s 72-qubit computer just 200 seconds." We think Google used the newly designed "Sycamore" processor that has 54 qubits installed. One was bad, so they only used 53 qubits.
As quoted on Google AI's website, "A research effort from Google AI that aims to build quantum processors and develop novel quantum algorithms to dramatically accelerate computational tasks for machine learning."
Google aims to offer cloud access to computers powered by its 72 qubit Bristlecone TM quantum processor.
Source: https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/semiconductors/design/google-team-builds-circuit-to-solve-one-of-quantum-computings-biggest-problems
Google aims to offer cloud access to computers powered by its 72 qubit Bristlecone TM quantum processor.
Source: https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/semiconductors/design/google-team-builds-circuit-to-solve-one-of-quantum-computings-biggest-problems
Thank you Kevin D. Kissell and FOSDEM19.org, Feb 2, 2019: "Quantum Computing at Google and in the Cloud"
Rigetti - Superconducting Qubits
Rigetti Computing, a full stack quantum computer manufacturer
In August 2018, Chad Rigetti announced their plan to build and deploy a 128-qubit system over the next 12 months, with investments at the application layer. They provide a Forest SDK to allow for cloud access to these systems.
Rigetti's Quantum Advantage Prize TM
Rigetti Computing "it will pay $1 million to anyone who can, according to CEO Chad Rigetti, use the company's Quantum Cloud Services to solve a useful problem in a way that is "better, faster or cheaper" than using a regular computer would be." |
Rigetti 16Q Aspen-1 (16 Qubits) |
For a chance to earn USD $1M, we asked to join the beta for Quantum Cloud Services and use Quamtum Machine Images (QMIs) that come pre-configured with the Rigetti Forest TM 2.0 SDK.
Intel Corp. - Superconducting & Si Spin Qubits (2 technologies)
Intel Corporation (Hardware & open source Simulator)
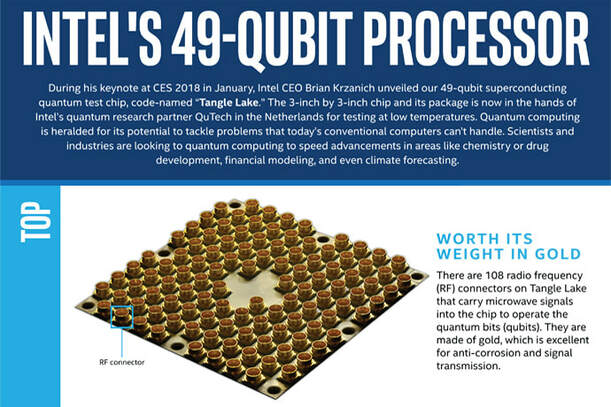
October 2019: Intel's is producing 49 qubit quantum processors in Hillsboro, Oregon at their 300-millimeter fabrication facility. This is their 3rd generation of processor. Commercial scale viability is set at 1,000,000 qubits. 3rd generation Tangle Lake quantum processors contain 49 superconducting qubits (technology 1) are are very large (3 inches square).
Spin qubits are a competing technology that holds promise because: 1) more closely resemble existing silicon semiconductor components, 2) need less cooling (1K vs ~20mK), 3) longer lasting coherence, 4) much smaller. The size could be the deal-breaker, as "a billion spin qubits could theoretically fit in one square millimeter of space."
Previously, Intel described how they were working to develop a commercially viable, full quantum stack, including hardware and software.
Please check back and we will provide more information and updates over time.
In the mean time...it may take a while to reach production quality and scale.
Intel sees commercial quantum production starting ~2025.
Jim Clarke calls 10 years (2029) to have 1 million qubits on a processor.
Spin qubits are a competing technology that holds promise because: 1) more closely resemble existing silicon semiconductor components, 2) need less cooling (1K vs ~20mK), 3) longer lasting coherence, 4) much smaller. The size could be the deal-breaker, as "a billion spin qubits could theoretically fit in one square millimeter of space."
Previously, Intel described how they were working to develop a commercially viable, full quantum stack, including hardware and software.
Please check back and we will provide more information and updates over time.
In the mean time...it may take a while to reach production quality and scale.
Intel sees commercial quantum production starting ~2025.
Jim Clarke calls 10 years (2029) to have 1 million qubits on a processor.
Intel also has a simulator (for several years) called Intel Quantum Simulator. According to Jim clarke, it can simulate ~ 30 qubits on your laptop. However, to simulate 40, you need a supercomputer (exponential growth in power needed). The feedback loop is to develop an algorithm, run it on the simulator, then run it on the hardware. For anything above a certain size, for example 49 qubit simulations, you need to figure out another way to verify the algorithm.
Intel's open source page: https://01.org/.
Intel's open source page: https://01.org/.
Tangle Lake (49 superconducting qubit test quantum processor). This was released in 2018.
This Intel chip is a big deal in a very small package. Details TBD (source, Intel's Newsroom, March 4, 2019.)
"A 2018 photo shows Intel’s new quantum computing chip balanced on a pencil eraser. Researchers started testing this “spin qubit chip” at the extremely low temperatures necessary for quantum computing: about 460 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. Intel projects that qubit-based quantum computers, which operate based on the behaviors of single electrons, could someday be more powerful than today’s supercomputers. (Credit: Walden Kirsch/Intel Corporation)"
"A 2018 photo shows Intel’s new quantum computing chip balanced on a pencil eraser. Researchers started testing this “spin qubit chip” at the extremely low temperatures necessary for quantum computing: about 460 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. Intel projects that qubit-based quantum computers, which operate based on the behaviors of single electrons, could someday be more powerful than today’s supercomputers. (Credit: Walden Kirsch/Intel Corporation)"
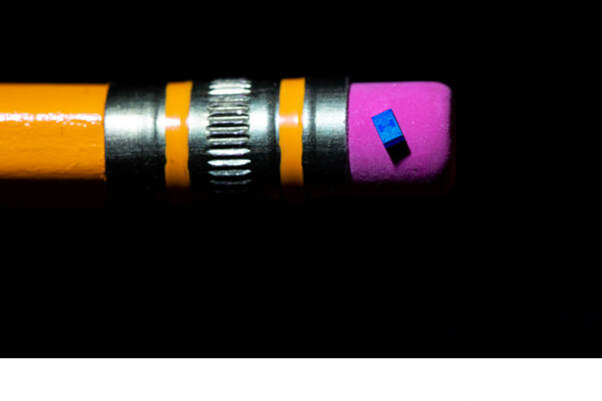
A 2018 photo shows Intel’s new quantum computing chip balanced on a pencil eraser. Researchers started testing this “spin qubit chip” at the extremely low temperatures necessary for quantum computing: about 460 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. Intel projects that qubit-based quantum computers, which operate based on the behaviors of single electrons, could someday be more powerful than today’s supercomputers. (Credit: Walden Kirsch/Intel Corporation)
IonQ - Trapped Ion Qubits
IonQ has deployed an 11 Qubit model and will start a cloud access model for it.
79 and 160 Qubit implementations are possible, but not yet tested.
Sources: https://ionq.com/
https://quantumcomputingreport.com/news/news-archive-2018/ionq-to-initiate-quantum-cloud-service-in-2019/
79 and 160 Qubit implementations are possible, but not yet tested.
Sources: https://ionq.com/
https://quantumcomputingreport.com/news/news-archive-2018/ionq-to-initiate-quantum-cloud-service-in-2019/
IonQ (founded in 2016, 34 employees, and 2 computers) has a goal of making small, but more accurate atomic quantum computers using trapped ions (in a vacuum), lasers, and superconducting qubits.
Based in College Park, Maryland (near University of Maryland). University of Maryland is part of a quantum consortium, has a quantum program, and Dr. Chris Monroe speak before the US House of Representatives in 2018.
We requested access and were put on a waiting list.
Honeywell Quantum Solutions - Trapped Ion Qubits
Honeywell Quantum Solutions (Trapped-ion qubit, gate-based system)
- As of March 12, 2019, Honeywell created three parallel operating zones which allows three different gate operations in three zones, simultaneously. They are testing first-generation systems.
- As of November 19, 2018, Honeywell Quantum Solutions (HQS) had started testing their first generation of commercial, micro-fabricated, trapped-ion qubit devices. They are evaluating 1D and 2D arrays. They are bringing together a full set of capabilities to design a future quantum computer.
- I cannot determine timing yet, but I do see investment from significant job postings. Their site lists 100+ employees in this group. They are hiring in the hard sciences and in engineering roles to design and build these systems.
Honeywell continues to hire...
"Honeywell Quantum Solutions is focused on developing the world's most advanced quantum computers, with 'full stack' capability from user interface software to the hardware layer and trapped ions. Our outstanding team of scientists and engineers leverages expertise in complex hardware and software control systems, advanced optics and lasers, magnetics, cryogenics, atomic physics, and ultra-high vacuum environments to design and build systems with best-in-class performance in terms of both fidelity and qubit count." Job Number req., 210201, Broomfield, Colorado US
Microsoft Azure Quantum
Microsoft, in November 2019, announced their strategy to provide access to Microsoft Azure and three quantum technologies.
Learn more here: https://cloudblogs.microsoft.com/quantum/2019/11/04/announcing-microsoft-azure-quantum/
We asked to join the Microsoft Azure Quantum preview. Will let you know what we find out!
Learn more here: https://cloudblogs.microsoft.com/quantum/2019/11/04/announcing-microsoft-azure-quantum/
We asked to join the Microsoft Azure Quantum preview. Will let you know what we find out!
Microsoft - Topological Qubits
Microsoft made its quantum development kit open source. Thank you
While Microsoft is researching a new type of qubit, it is helping clients learn how to think and code in a quantum inspired way.
"Microsoft has been working on scalable quantum computing for nearly two decades, creating its first quantum computing group—known as Station Q—in 2006."
"Microsoft has been working on scalable quantum computing for nearly two decades, creating its first quantum computing group—known as Station Q—in 2006."
According to Dr. Julie Love, Director Quantum Business Develop at Microsoft, at a speech at London Tech Week, "“Microsoft is working on the only scalable solution, one that will run seamlessly on the Azure cloud, and be much more immune to errors. The truth is that not all qubits are equal; most are inherently unstable and susceptible to error-creating noise from the environment. Our approach uses topological qubits specifically for their higher accuracy, lower cost and ability to perform long enough to solve complex real-world problems.”
Microsoft released a Quantum Development Kit (Q#) so developers can write quantum programs and run them on an ~30 qubit simulator (they run on classical computers). “We have released the Quantum Development Kit so developers can learn to program a quantum computer and join us on this journey,” Dr. Julie Love stated.
In a 2018 quote from the BBC.com, "We will have a commercially relevant quantum computer - one that's solving real problems - within five years," says Dr Julie Love, Microsoft's director of quantum computing business development. "What it allows us to do is solve problems that with all of our supercomputers running in parallel would take the lifetime of the universe to solve in seconds, hours or days."
Source: https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-43580972
“Five years from now, we will have a commercial quantum computer,” says Dr. Todd Holmdahl, Microsoft VP and PhD in quantum physics from Yale (and ex-McKinsey & Company).
Source: https://www.barrons.com/articles/microsoft-we-have-the-qubits-you-want-1519434417
We will try out the QDK and run programs on the simulator.
Please check back for more information, as we learn more.
While you wait...here is a marketing video from Microsoft. Sounds like how we used to speak about quantum :)
Microsoft released a Quantum Development Kit (Q#) so developers can write quantum programs and run them on an ~30 qubit simulator (they run on classical computers). “We have released the Quantum Development Kit so developers can learn to program a quantum computer and join us on this journey,” Dr. Julie Love stated.
In a 2018 quote from the BBC.com, "We will have a commercially relevant quantum computer - one that's solving real problems - within five years," says Dr Julie Love, Microsoft's director of quantum computing business development. "What it allows us to do is solve problems that with all of our supercomputers running in parallel would take the lifetime of the universe to solve in seconds, hours or days."
Source: https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-43580972
“Five years from now, we will have a commercial quantum computer,” says Dr. Todd Holmdahl, Microsoft VP and PhD in quantum physics from Yale (and ex-McKinsey & Company).
Source: https://www.barrons.com/articles/microsoft-we-have-the-qubits-you-want-1519434417
We will try out the QDK and run programs on the simulator.
Please check back for more information, as we learn more.
While you wait...here is a marketing video from Microsoft. Sounds like how we used to speak about quantum :)
https://news.microsoft.com/innovation-stories/quantum-computing-mri-cancer-treatment/
Microsoft is helping apply 'quantum inspired algorithms' that run on classical computers to help Case Western University do better and more accurate cancer scans to see if chemo treatments are working after just one dose, as opposed to waiting 6 months. This is very helpful medical work in treating cancer. Thanks Microsoft!
Microsoft is helping apply 'quantum inspired algorithms' that run on classical computers to help Case Western University do better and more accurate cancer scans to see if chemo treatments are working after just one dose, as opposed to waiting 6 months. This is very helpful medical work in treating cancer. Thanks Microsoft!
Fujitsu - Digital Annealer (quantum inspired)
Fujitsu Quantum-Inspired Digital Annealer, also available in a cloud service
A great research report on potential uses of quantum computing, urgency, and how 300 surveyed companies don't want to wait!
https://www.fujitsu.com/us/about/resources/news/press-releases/2019/fai-20190515.html
https://www.fujitsu.com/us/about/resources/news/press-releases/2019/fai-20190515.html
Solve Combinatorial Optimization Problems on a highly connected digital (classical) computer that is 'quantum inspired.' This system runs at normal data center temperatures. This is like a quantum simulator.
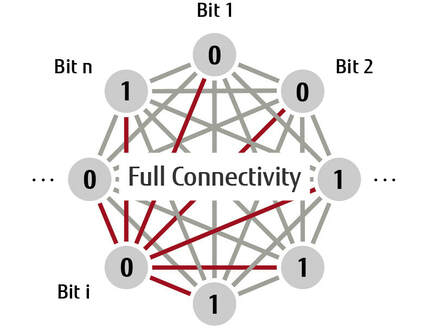
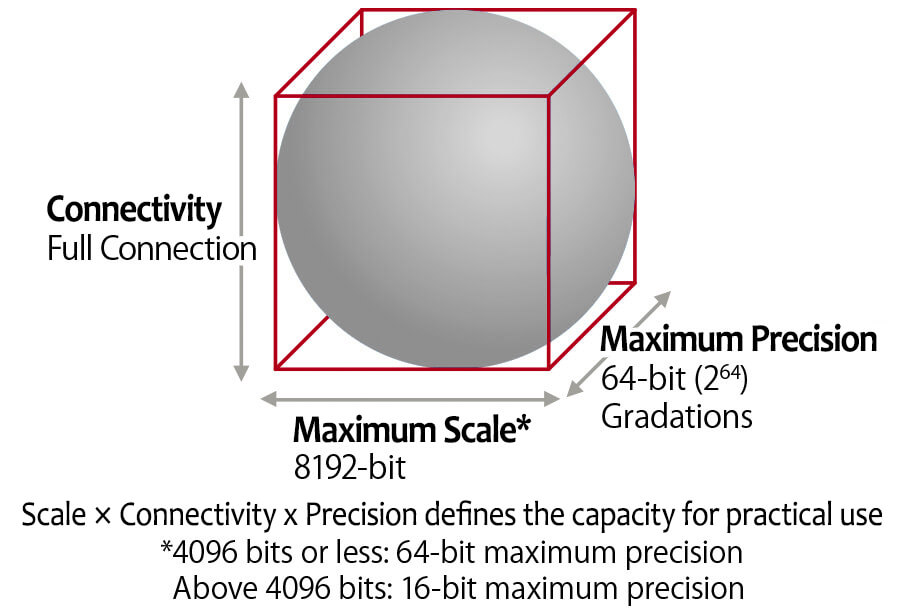
Fujitsu is offering a set of hardware, software and services around this new platform. On October 7, 2019, we read that Fujitsu has a new, 2nd generation processor (DAU) that uses higher density circuits. It can solve problems of a scale that can be expressed in up to 1,024 bits. Throughput increased by a factor of 100. Connectivity between bits grew from 1,024 to 8,192 and coupling accuracy grew from 16 bits to 64 bits.
In October 7, 2019, we also read that Fujitsu and Multiverse partnered to solve optimization problems for business, using Fujitsu's technology solution. Targeted at banking, they will attempt to minimize risk (correlation, credit and liquidity) while maximizing expected returns (arbitrage and investment returns).
A recent May 15, 2019 Press Release includes a few more use cases, and supporting market data cases for their 'inspired by quantum' Digital Annealer. In one case, Fujitsu is scheduling the best possible path for production for robots in the paint shop for an premium automotive supplier with 64 seams. The number of possible trip combinations exceeds the assumed number of atoms in the universe, and Fujitsu is helping them flow more cars through the 'paint shop' lowering the cost per vehicle.
We need to see whether their system can solve "large enough" problems to be useful. At a recent D-Wave conference, we learned from one graduate student that they could not run a portfolio optimization with 20 assets on a D-Wave quantum annealer. Twenty assets optimized could be a benchmark for these teams.
Fujitsu is offering a set of hardware, software and services around this new platform. On October 7, 2019, we read that Fujitsu has a new, 2nd generation processor (DAU) that uses higher density circuits. It can solve problems of a scale that can be expressed in up to 1,024 bits. Throughput increased by a factor of 100. Connectivity between bits grew from 1,024 to 8,192 and coupling accuracy grew from 16 bits to 64 bits.
In October 7, 2019, we also read that Fujitsu and Multiverse partnered to solve optimization problems for business, using Fujitsu's technology solution. Targeted at banking, they will attempt to minimize risk (correlation, credit and liquidity) while maximizing expected returns (arbitrage and investment returns).
A recent May 15, 2019 Press Release includes a few more use cases, and supporting market data cases for their 'inspired by quantum' Digital Annealer. In one case, Fujitsu is scheduling the best possible path for production for robots in the paint shop for an premium automotive supplier with 64 seams. The number of possible trip combinations exceeds the assumed number of atoms in the universe, and Fujitsu is helping them flow more cars through the 'paint shop' lowering the cost per vehicle.
We need to see whether their system can solve "large enough" problems to be useful. At a recent D-Wave conference, we learned from one graduate student that they could not run a portfolio optimization with 20 assets on a D-Wave quantum annealer. Twenty assets optimized could be a benchmark for these teams.
Sales target: Fujitsu is aiming for 100.0 billion yen in revenue over five years through fiscal 2022.
Competition Details: In March 2019 ran a Japan contest with Topcoder to leverage "Digital Annealer" to solve an optimization problem and present the optimal division method for enabling swift and accurate calculations for a large-scale problem that cannot be solved with a single calculation. Prize total USD: $16,000
Source: https://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/resources/news/press-releases/2018/0515-01.html
https://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/resources/news/press-releases/2019/0115-01.html
Competition Details: In March 2019 ran a Japan contest with Topcoder to leverage "Digital Annealer" to solve an optimization problem and present the optimal division method for enabling swift and accurate calculations for a large-scale problem that cannot be solved with a single calculation. Prize total USD: $16,000
Source: https://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/resources/news/press-releases/2018/0515-01.html
https://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/resources/news/press-releases/2019/0115-01.html
ATOS - Quantum Simulation
ATOS Quantum Learning Machine (Atos QLM) - software & hardware platform to simulate quantum computing; simulates ~40 qubits
"Atos... has developed the Atos Quantum Learning Machine (Atos QLM) which allows programmers to write software without waiting for a general-purpose quantum computer to be built. The QLM can do that because it simulates the laws of physics that govern quantum computing."
"For example, a programmer can state that she wants to simulate interactions with a 16-qubit quantum computer, and the platform will behave accordingly. As of July 2018, the QLM was capable of simulating up to 41 qubits."
"According to the Atos executives I interviewed, their QLM sells really well in the United States."
According to inside sources at ATOS, there is a working QLM system at Argonne National Lab.
The classical architecture makes great sense to us at Chicago Quantum.
Atos announced 40 qubit simulation in 2017. Wonder if they upgraded since then?
"For example, a programmer can state that she wants to simulate interactions with a 16-qubit quantum computer, and the platform will behave accordingly. As of July 2018, the QLM was capable of simulating up to 41 qubits."
"According to the Atos executives I interviewed, their QLM sells really well in the United States."
According to inside sources at ATOS, there is a working QLM system at Argonne National Lab.
The classical architecture makes great sense to us at Chicago Quantum.
Atos announced 40 qubit simulation in 2017. Wonder if they upgraded since then?
Xanadu - Silicon Photonic Qubits
Toronto Startup using photonics (not electrons) to build a full-stack quantum computing capability. On July 16, 2019, we learned they did a public demonstration over a cloud connection.
According to their website: "Xanadu designs and integrates quantum silicon photonic chips into existing hardware to create truly full-stack quantum computing." Looks like a very technical start-up, well staffed and funded.
Xanadu: Software environments include Python libraries they call Strawberry Fields (TM) and PennyLane (TM) for use in software development.
World first! pre-alpha public demo of the @XanaduAI photonic quantum cloud! By Nathan Killoran for this years @creativedlab #historic #CloudComputing #QuantumComputing pic.twitter.com/JeE32ciyD8
— Christian Weedbrook (@c_weedbrook) July 16, 2019
There is also a competition that we learned about. They will award CAD $1,000 to the best idea in each of three categories: Education, Software and Research. Entries close 30 August, 2019. Enter and learn more here: https://pennylane.ai/competition/#awards
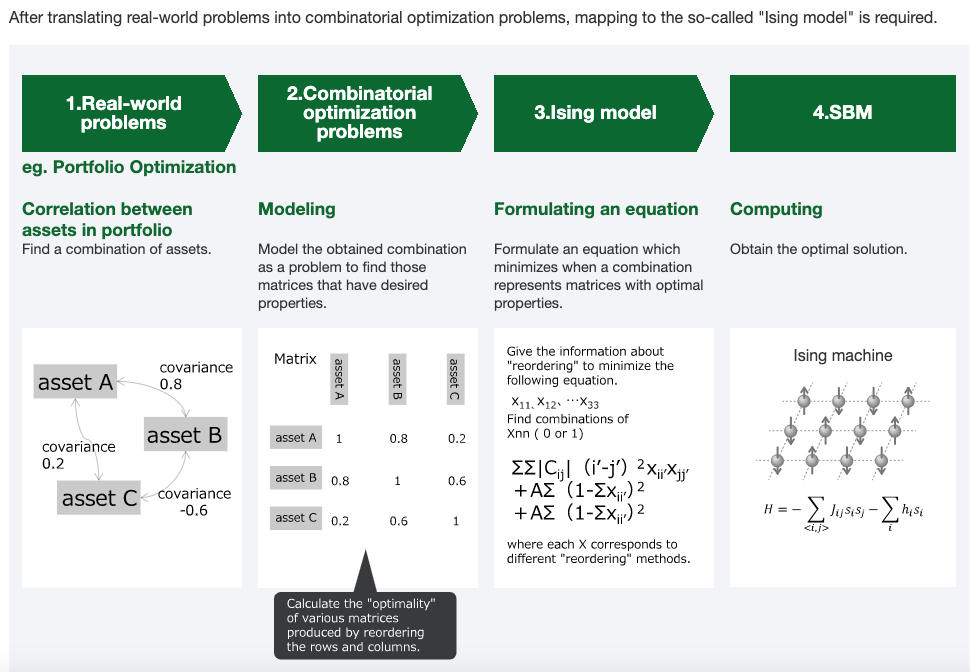
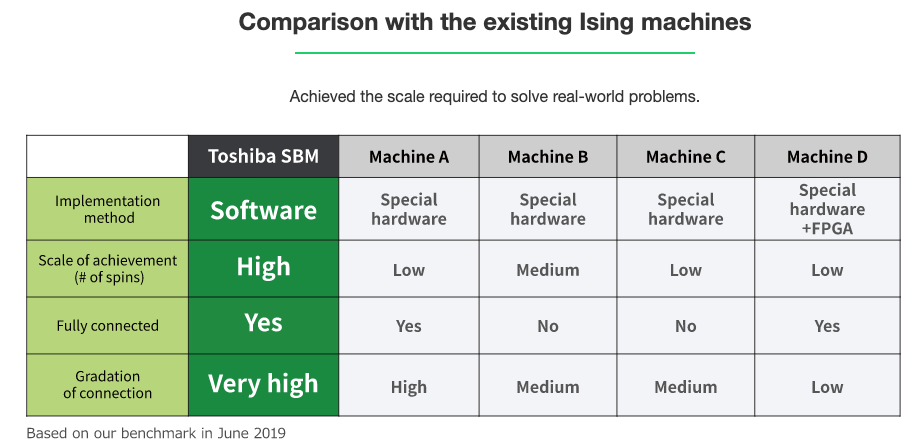
Toshiba Digital Solutions Corporation
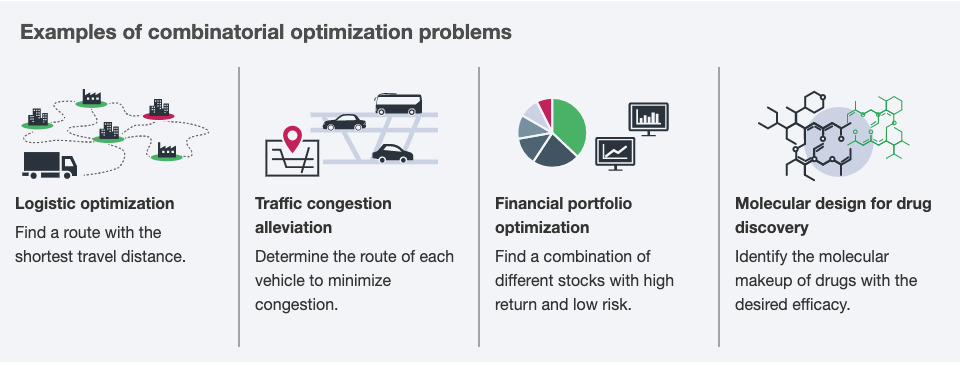
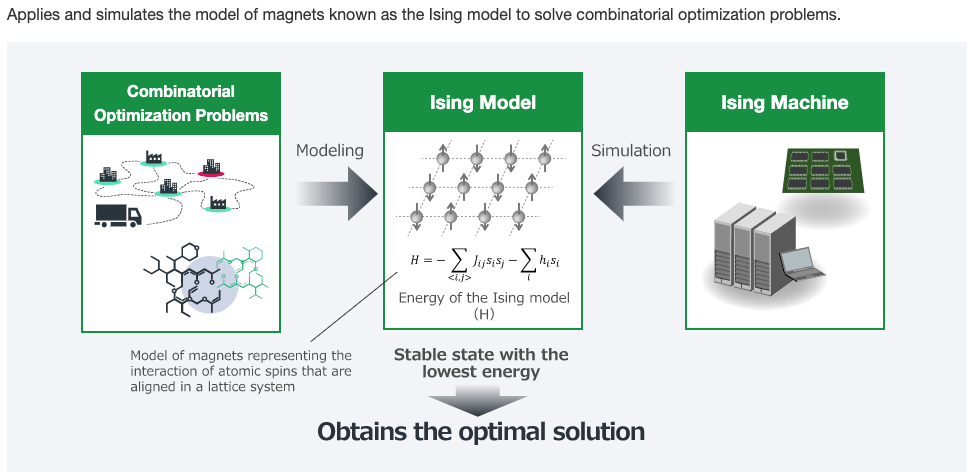
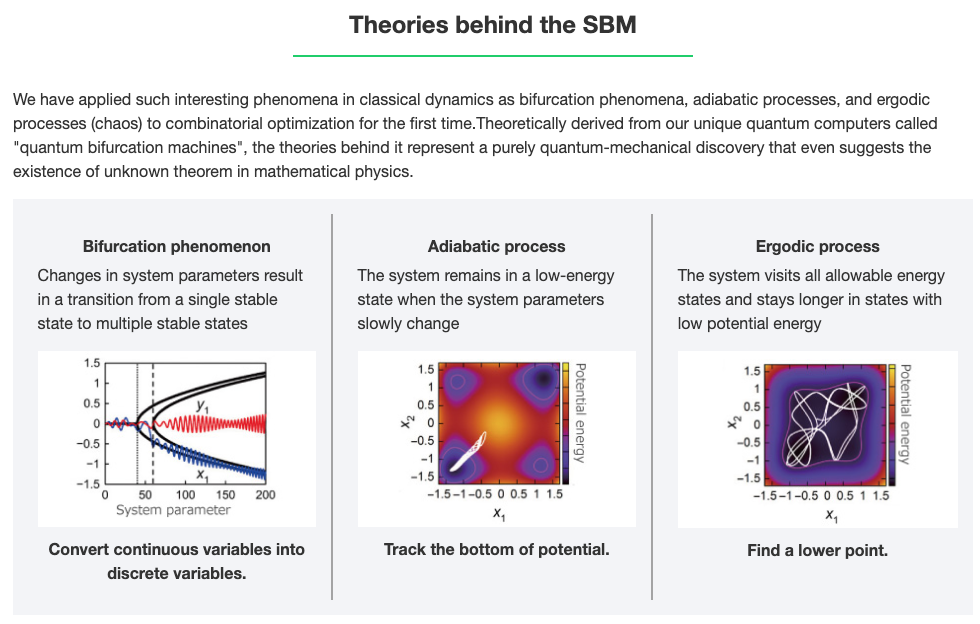
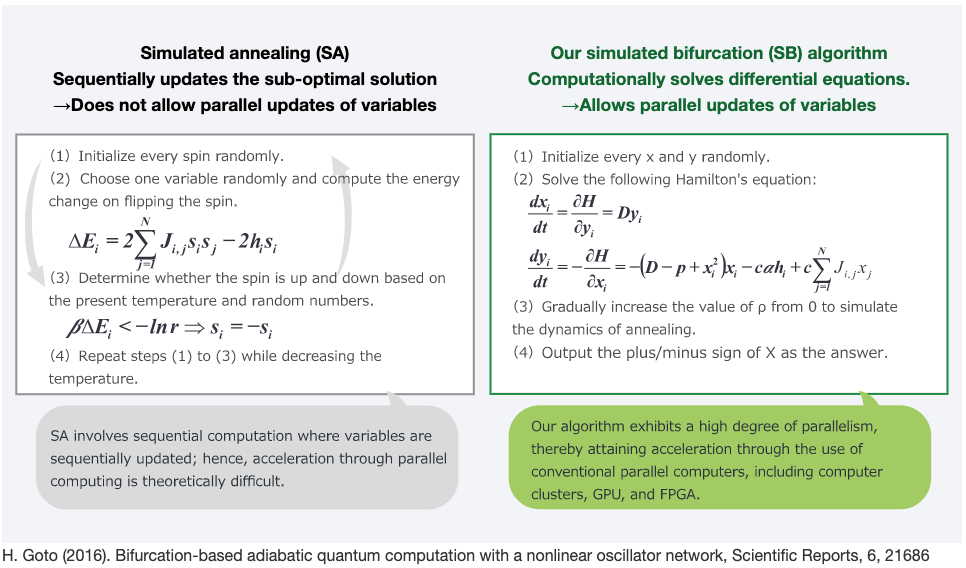
Simulated Bifurcation Machine (SBM) applies an Ising Model to combinatorial optimization problems to obtain the best answer it can.
There is a story here to follow about why Toshiba's solution is fast, and how it would be used. We need to try the SBM ourselves!
In Goto's 2019 paper abstract, we read that this SBM technology can obtain good, approximate solutions in an all-to-all connected 2000-node MAX-CUT problem in 0.5 ms (10x faster than a coherent Ising machine).
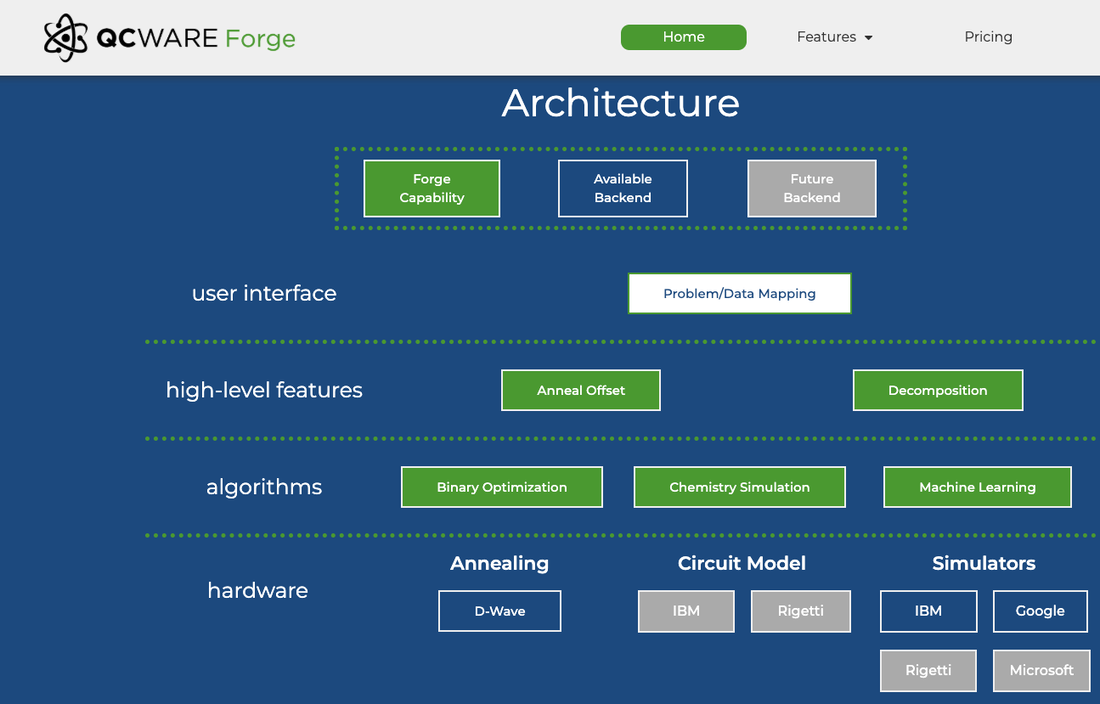
QCWare Forge - Quantum Computing as a Service (QCaaS)
Works across annealing, circuit and simulator services
Sign up for your free trial today. We did.
Alpine Quantum Technologies GmbH - Trapped Ion Qubits
A start-up led by three prominent physicists with significant experimental experience with ion trap technologies.
AQT has a 5 qubit trapped ion system hosted at the University of Innsbruck. IBM Qiskit can be used to run jobs on it.
They have a 20 qubit trapped ion system that is used for chemistry experiments.
"IBM open-source Qiskit quantum computing framework has been designed to be extensible and to support research beyond the IBM quantum systems based on superconducting qubits. The company recently added support in Qiskit for trapped ion-based quantum computing devices and enabled access to the five-qubit trapped ion device at the University of Innsbruck (UIBK) hosted by Alpine Quantum Technologies (AQT)."
We understand CIRQ can also be used to control the AQT system. This makes this a very open and accessible system.
They have a 20 qubit trapped ion system that is used for chemistry experiments.
"IBM open-source Qiskit quantum computing framework has been designed to be extensible and to support research beyond the IBM quantum systems based on superconducting qubits. The company recently added support in Qiskit for trapped ion-based quantum computing devices and enabled access to the five-qubit trapped ion device at the University of Innsbruck (UIBK) hosted by Alpine Quantum Technologies (AQT)."
We understand CIRQ can also be used to control the AQT system. This makes this a very open and accessible system.
IDQuantique - QKD & QRNG Hardware
ID Quantique: QKD and Random Number Generation
South Korea (SK) Telecom bought 50% of Swiss-based IDQ for 70 billion Won (equivalent to USD $65M).
Fundamentally random number generation.
According to ZDNet, "IDQ was founded in 2001 and launched a quantum random number generator in 2002, and later quantum key distribution systems in 2006. It has customers in North America, Europe, and the Middle East.
SK Telecom formed its own quantum technology laboratory in 2011 and developed a 5x5 millimetere quantum random number generator last year.
The two have partnered since 2016 and the telco has invested $2 million to develop a quantum random number generator chip.
Global quantum cryptography communications will grow to be worth $24.75 billion in 2025, according to Market Research Media."
https://www.zdnet.com/article/sk-telecom-buys-half-of-swiss-quantum-safe-crypto-firm-for-65m/
Fundamentally random number generation.
According to ZDNet, "IDQ was founded in 2001 and launched a quantum random number generator in 2002, and later quantum key distribution systems in 2006. It has customers in North America, Europe, and the Middle East.
SK Telecom formed its own quantum technology laboratory in 2011 and developed a 5x5 millimetere quantum random number generator last year.
The two have partnered since 2016 and the telco has invested $2 million to develop a quantum random number generator chip.
Global quantum cryptography communications will grow to be worth $24.75 billion in 2025, according to Market Research Media."
https://www.zdnet.com/article/sk-telecom-buys-half-of-swiss-quantum-safe-crypto-firm-for-65m/
USE CASE: SK Telecom announced on March 18, 2019, "that it applied ID Quantuque's Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG) to its 5G authentication center (AuC) to prevent hacking and ensure quantum-safe security." Plans to install QRNG to AuC of its LTE network in April 2019. IMHO, this is a big deal.
Furthermore, SK Telecom is playing a pivotal role in global standardization of QKD and QRNG technologies at ITU-T. In February 2019, SK Telecom’s two new technologies related to QKD have been selected as work items by ITU-T’s Study Group 17 (SG17), which coordinates security-related work across all ITU-T Study Groups. Combining these two work items with the two on-going work items on QKD and QRNG technologies it proposed in July 2018, SK Telecom is currently leading a total of four meaningful work items in SG 17.
Furthermore, SK Telecom is playing a pivotal role in global standardization of QKD and QRNG technologies at ITU-T. In February 2019, SK Telecom’s two new technologies related to QKD have been selected as work items by ITU-T’s Study Group 17 (SG17), which coordinates security-related work across all ITU-T Study Groups. Combining these two work items with the two on-going work items on QKD and QRNG technologies it proposed in July 2018, SK Telecom is currently leading a total of four meaningful work items in SG 17.
Amazon Web Services (building a team)
In May and June 2019, AWS posted 2 jobs for Software Development Engineers (in Seattle, WA) "to identify and commercialize cutting edge quantum technologies, including hardware, software and classical simulation of quantum algorithms." Another quote: "...and join the team at its inception."
According to Computerworld in December 2018, Amazon appointed Simone Severini, professor of Physics of Information at University College London (UKI) as AWS's Director, Quantum Computing in November 2018. We asked Dr. Severini to connect.
Remember Jeff Barr's announcement of a production Quantum Compute Cloud (QC2) in 2010?
More to come, stay tuned for updates.
According to Computerworld in December 2018, Amazon appointed Simone Severini, professor of Physics of Information at University College London (UKI) as AWS's Director, Quantum Computing in November 2018. We asked Dr. Severini to connect.
Remember Jeff Barr's announcement of a production Quantum Compute Cloud (QC2) in 2010?
More to come, stay tuned for updates.
AT&T investing into INQNET / Caltech to develop quantum networks
This is very early stage work to connect quantum computers and quantum qubits together - maintaining entanglement and allowing parallel and clustered processing. This allows quantum computers to become quantum computing systems.
RAMBUS Cryogenic DRAM - can store SFQ processor data
So much to talk about here...the DRAM is not QRAM (data not entangled, nor in superposition), but nearby and operating at reasonable latency levels. A 2017 paper suggests running DRAM in close proximity to the Quantum processor (a few levels away in the dilution refrigerator) at 85K for the best energy/performance/latency trade-offs.
Source: https://www.rambus.com/blogs/exploring-future-memory-requirements-for-quantum-computing-2/
https://www.rambus.com/emerging-solutions/cryogenic-memory/
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/98967
https://info.rambus.com/the-case-for-cold-dram?hsCtaTracking=bba6a731-f75f-46c0-af91-0a38ea44e9ad%7C889f2326-319e-4d0c-b3c8-8a74570086c9
https://info.rambus.com/hubfs/rambus.com/Gated-Content/Cryogenic%20Memory/Case_for_Cold_DRAM.pdf?hsCtaTracking=3af7ddaa-6036-4a4b-8638-d5884508d2a2%7C1a730949-d8c2-4a16-bab2-9daec63454ba
Source: https://www.rambus.com/blogs/exploring-future-memory-requirements-for-quantum-computing-2/
https://www.rambus.com/emerging-solutions/cryogenic-memory/
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/98967
https://info.rambus.com/the-case-for-cold-dram?hsCtaTracking=bba6a731-f75f-46c0-af91-0a38ea44e9ad%7C889f2326-319e-4d0c-b3c8-8a74570086c9
https://info.rambus.com/hubfs/rambus.com/Gated-Content/Cryogenic%20Memory/Case_for_Cold_DRAM.pdf?hsCtaTracking=3af7ddaa-6036-4a4b-8638-d5884508d2a2%7C1a730949-d8c2-4a16-bab2-9daec63454ba
Open Source: GitHubThere are numerous GitHub projects highlighting Python or Jupyter Notebooks, and quantum code.
Chicago Quantum started a new GitHub project. |
Other Activities by Government and Standard Setting Bodies
Quantum Flagship, founded by the European Union. The European Union has agreed to spend EUR 1 Billion over 10 years to promote industry and academic applications of quantum computing. Learn more here. We signed up as a participant, and hope to engage.
October 29, 2018, there was a kick off of this 10-year, €1bn European Commission (EC) initiative. The flagship’s initial, €132m phase runs through September 2021.
October 29, 2018, there was a kick off of this 10-year, €1bn European Commission (EC) initiative. The flagship’s initial, €132m phase runs through September 2021.
IEEE
US Government led consortium, administered by SRI Corporation
US National Institute of Science and Technology (NIST) has a quantum focused effort.